Small molecule drugs are biologically active compounds synthesized with organic chemistry approaches, with molecular weight below 1000 Da. They have excellent pharmacological functions and tissue distribution properties, allowing for broad therapeutic indications. They also have good pharmacokinetic profiles and chemical stability, with the advantages of convenient storage and transportation. They are orally administered; hence it is easier to get patients to comply with treatments. Furthermore, they can be designed in novel and creative ways for differentiation and unmet medical needs. For these reasons, small molecules exert huge therapeutic potential in various disease areas and continue to be the mainstay of the pharmaceutical industry.
Focusing on current urgent and unmet medical needs, the Innovative Small Molecules Research Institute are committed to developing new small molecule therapeutics. We aim for comprehensive understandings of the disease biology and establishment of innovative, high-value portfolio.
Our pipeline covers 5 major disease areas, including kidney diseases, oncology, respiratory and infectious diseases, and neurological disorders. Our team of scientists bring together deep expertise in discovery biology, medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, ADME, toxicology, formulation and process development, regulatory affairs and clinical development. We combine our unique knowledge and experiences with cutting-edge technologies including chemo-informatics, molecular biology, computer-assisted drug design, artificial intelligence and machine learning, to gain speed and improve success rates of small molecule screening and optimization.
| Pipeline | S/N | Product number | Product introduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney Diseases |
1 | JMKX000189 | Multiple organ autoimmune diseases have significant advantages in efficacy and safety |
| 2 | JMKX003142 | Significant advantages in efficacy and safety for hereditary chronic kidney disease | |
| 3 | JMKX003002 | Chronic kidney disease complicated with metabolic diseases, with significant advantages in preclinical data | |
| 4 | JMKX004649 | Common immune nephropathy with significant unmet needs | |
| Oncology | 5 | JMKX001899 | Non small cell lung cancer, good brain penetration, high safety, and potential for breakthrough therapy |
| 6 | JMKX000197 | Targeting FIC and First Indication, local manifestations have therapeutic advantages | |
| 7 | JMKX003948 | Simultaneously inhibiting multiple tumor specific growth factors, effective against multiple tumor species | |
| 8 | JMKX003561 | Innovative targets, preclinical data shows significant inhibition of specific cancer species growth | |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 9 | JMKX001149 | Treat and prevent thrombotic diseases while reducing potential bleeding risks |
| 10 | JMKX003142 | Through intravenous administration, suitable for the treatment scenario of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases | |
| Respiratory Diseases | 11 | JMKX003801 | Targeting drug-resistant bacterial infections, a novel broad-spectrum approach β- lactamase inhibitor |
| 12 | JMKX003676 | The target is fungal infection, with low liver toxicity and better safety than existing drugs | |
| Pain | 13 | JMKX000623 | It has a significant inhibitory effect on various pain models and has entered the clinical stage |
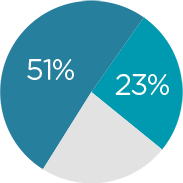
The Innovative Small Molecules Research Institute has a team of 150 scientists, of whom 23% hold PhD degree and 51% hold MS degrees. The management team are seasoned scientists trained overseas with rich experience from leading pharmaceutical companies worldwide. They have accumulated broad and deep knowledge via leading multiple high-profile programs in the past.

patients with CVD in China
mortality rate

new cancer cases very year in China
Malignant tumor has been a major threat. Currently around 4 million new cases are reported every year in China.
The small molecule anti-tumor drugs are developed against oncogenes. Once absorbed, these drugs specifically bind to their targets, leading to the apoptosis induction and proliferation inhibition of tumor cells. Targeted drugs show much higher specificity, better efficacy, and less toxicity, as compared to conventional chemotherapeutic agents.
CKD patients in China
The chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common chronic disease in China, and current patient population is about 119.5 million. The progression of CKD is affected by multiple factors, including hemodynamic changes, metabolic disorders, inflammation, and fibrosis. In addition to existing prophylactic approaches of lowering blood pressure (controlling hemodynamics) and blood sugar (improving metabolism), further novel effective therapeutics are needed to slow down CKD progression. We are working towards this goal by developing small molecule drugs to inhibit hyperactivation of mineralocorticoid receptors and overexpression of inflammatory factors and cytokines, to ultimately reduce inflammation and fibrosis
deaths due to antibiotic resistance every year worldwide
The small molecule anti-bacterial drugs interfere with the metabolism of pathogenic microorganisms, inhibiting critical synthetic pathways for nucleic acids, proteins, cell membranes and cell wall. As compared to conventional anti-bacterial agents, the novel molecules we’ve developed are specifically designed to tackle multidrug resistance. They showed broader spectrum, higher bactericidal activity, and better safety profile in human. These molecules are effective against several multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria, providing a potentially better option for treating MDR bacterial infections and severe systemic infections.